
By
- Robert Sheldon
What is a megabyte?
A megabyte is a unit of data capacity that is equal to 1,000,000 bytes in decimal notation (base 10) or 1,048,576 bytes in binary notation (base 2). The base-10 amount is also represented as 106 or 10002 bytes, and the base-2 amount is represented as 220 or 10242 bytes. Mega comes from the Greek word megas, which means large or great. In computing, mega is used for one million or an amount close to that.
Megabyte is a multiplier of byte, which is the smallest unit of addressable memory in most computer architectures. A byte is typically made up of eight binary digits (bits). The eight-bit byte is considered today's de facto standard for byte length, although that number can vary depending on the hardware. Eight bits are also referred to as an octet, so a standard byte is sometime called an octet. A megabyte based on standard bytes is equal to 8,000,000 bits in decimal notation or 8,388,608 in binary notation.
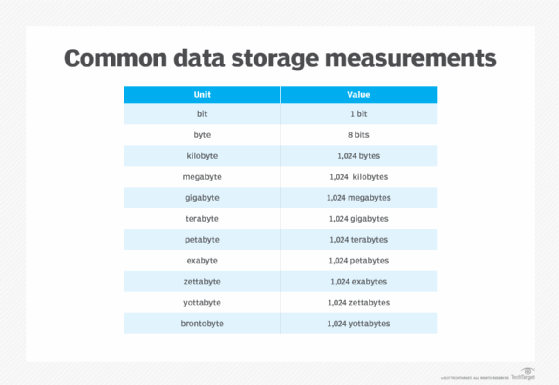
The megabyte is one of several multipliers used to represent larger numbers of bytes. For example, a kilobyte (KB) is equal to 1,000 bytes (decimal) or 1,024 bytes (binary). As such, a megabyte is equal to 1,000 KB (decimal) or 1,024 KB (binary). There are also byte multipliers that go much higher than megabytes, such as gigabyte (GB), terabyte (TB) and petabyte (PB):
- A gigabyte is equal to 10003 bytes (decimal) or 10243 bytes (binary), which can also be expressed as 1,000 MB and 1,024 MB, respectively.
- A terabyte is equal to 10004 bytes (decimal) or 10244 bytes (binary), which can also be expressed as 1,000,000 MB and 1,048,576 MB, respectively.
- A petabyte is equal to 10005 bytes (decimal) or 10245 bytes (binary), which can also be expressed as 1,000,000,000 MB and 1,073,741,824 MB, respectively.
At one time, the megabyte was used extensively across the industry as a measure for storage and memory data capacities. As these capacities have increased, megabyte is used less frequently for storage and memory, which are now usually measured in gigabytes or, in the case of storage, terabytes.
Even so, the megabyte is still used where smaller measurements are required, such as when referring to file sizes or disk usage. For example, a novel might take up around 1 MB of disk space, a high-resolution photo might require more than 5 MB of space and a long audio book might use up to 500 MB of storage. In addition, some storage media are still measured in megabytes, such as the CD-ROM, which can hold 700 MB of data.
Megabyte vs. megabit
The megabyte is sometimes used when referring to data transfer rates. For instance, a USB flash drive might support transfers speeds up to 400 megabytes per second (MBps). Megabytes per second is often confused with megabits per second (Mbps), especially when abbreviations are used. It's not uncommon to see megabytes per second abbreviated as Mbps. This can sometimes make it difficult to know which one is correct.
Megabits per second is specific to the number of bits, not the number of bytes. A megabit (Mb) is equal to 1,000,000 bits (decimal) or 1,048,576 bits (binary). It is one-eighth the size of a megabyte. In other words, 1 MB equals 8 Mb. The megabit is generally used as a measure for the amount of data being transferred over a network, as opposed to being used to describe storage capacities.
Data at rest is typically measured in bytes, or more precisely, byte multipliers such as megabytes or larger. However, the byte -- and, by extension, the megabyte -- can also refer to storage bandwidth or throughput or to data being transferred across a network. For example, MBps might be used to refer to a storage product's data transfer rate, which indicates the speed at which data can move to or from the device.

Decimal vs. binary
Over the years, the dual nature of byte multipliers such as megabyte has caused both confusion and frustration across the industry, not only when it comes the MBps vs. Mbps, but in other ways as well. Computer, storage and network systems can use either type of notation and it's not always clear which one they have chosen.
For example, a manufacturer might show the capacity of a flash storage product as 900 GB, but when the drive is attached to a computer, the operating system shows the capacity at about 858 GB. Is the difference because the OS and storage vendor are using different notation types, or is there a problem somewhere in the system?
In the early days of computing, when capacities were relatively small, the differences between decimal and binary measurements were considered insignificant. Back then, memory and storage were measured in terms of kilobytes, not megabytes or larger, and the differences between the decimal and binary measures caused little concern. A kilobyte is equal to 1,000 bytes in binary notation and 1,024 bytes in decimal notation, so the difference between the two measurements is only 24 bytes. As capacities increased, however, those differences became much more pronounced.
Decimal notation is a base-10 system. A megabyte in decimal notation equals 106 bytes, or 1,000,000 bytes. Binary notation is a base-2 system. A megabyte in decimal notation equals 220 bytes, or 1,048,576 bytes. The difference between the two is 48,576 bytes, or around 49 KB, about the size of a simple eight-page word processor document. At 500 MB, that difference grows to over 24 MB. Although this might not seem like much, such a difference could cause concern for an organization that stores highly sensitive data and can't account for the 24 MB discrepancy.

Over the years, an effort has been underway to address the confusion caused by having two different approaches to byte multipliers. In 1999, the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) published a standard that defined a new set of prefixes for base-2 multipliers, leaving base-10 multipliers unchanged. According to the new standard, a megabyte (MB) is equal to exactly 106 bytes, or 1,000,000 bytes, and a mebibyte (MiB) is equal to exactly 220 bytes, or 1,048,576 bytes.
Since the IEC's publication, other standards organizations have adopted the IEC standard for multiplier prefixes, including the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers and NIST. Despite their support, however, the industry has been slow to adopt the new standard, so there is still a fair amount of confusion around these issues. Fortunately, some vendors have started using mebibyte and the other base-2 multipliers, where applicable, helping to bring clarity to the multiplier issue, at least in some quarters.
See how to convert binary to decimal and vice versa and learn about binary-coded decimal and how it is used. Check out binary and hexadecimal numbers explained for developers.
This was last updated in December 2023
Continue Reading About megabyte (MB)
- The future of data storage must handle heavy volume
- Best options for video data storage include cloud, tape
- How to develop and implement a data storage plan
Related Terms
- DIMM (dual in-line memory module)
- DIMM, or dual in-line memory module, is a type of computer memory that is natively 64 bits, enabling fast data transfer.Seecompletedefinition
- RAID 3 (redundant array of independent disks 3)
- RAID 3 (redundant array of independent disks 3) is a RAID configuration that uses a parity disk to store the information ...Seecompletedefinition
- removable media
- Removable media is any type of storage device that can be removed from a computer while the system is running. Removable media ...Seecompletedefinition
Dig Deeper on Storage architecture and strategy
- Types of bytes: Units of memory explainedBy: Kaitlin Herbert
- zebibyte (ZiB)By: StaceyPeterson
- yobibyte (YiB)By: StaceyPeterson
- pebibyte (PiB)By: StaceyPeterson